A high-performance transportable fountain clock is attractive for use in laboratories with high-precision time-frequency measurement requirements. This Letter reports the improvement of the stability of a transportable rubidium-87 fountain clock because of an optimization of temperature characteristics. This clock integrates its physical packaging, optical benches, microwave frequency synthesizers, and electronic controls onto an easily movable wheeled plate. Two optical benches with a high-vibration resistance are realized in this work. No additional adjustment is required after moving them several times. The Allan deviation of the fountain clock frequency was measured by comparing it with that of the hydrogen maser. The fountain clock got a short-term stability of 2.3×10 13 at 1 s and long-term stability on the order of 10 16 at 100,000 s.
For most atom interferometers, the vibration isolation unit is applied to reduce vibration noise. In our experiment, instead of isolation, the vibration signals are monitored, and combining with the sensitive function, the compensation phase shift for the atom interferometer is obtained. We focus on the correction over a wide spectrum rather than on “monochromatic” frequencies. The sensitivity of the atom gravimeter can be upgraded by a factor of more than two. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the atom interferometer can still produce a good measurement result without passive vibration isolation in extremely noisy environments by using vibration compensation.
Atomic Doppler broadening thermometry (DBT) is potentially an accurate and practical approach for thermodynamic temperature measurement. However, previous reported atomic DBT had a long acquisition time and had only been proved at the triple point of water, 0°C, for the purpose of determination of the Boltzmann constant. This research implemented the cesium atomic DBT for fast room temperature measurement. The Cs133 D1 (6S1/2 → 6p1/2 transition) line was measured by direct laser absorption spectroscopy, and the quantity of thermal-induced linewidth broadening was precisely retrieved by the Voigt profile fitting algorithm. The preliminary results showed the proposed approach had a 4 min single-scan acquisition time and 0.2% reproducibility. It is expected that the atomic DBT could be used as an accurate, chip-scale, and calibration-free temperature sensor and standard.
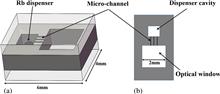
As the key part of chip-scale atomic clocks (CSACs), the vapor cell directly determines the volume, stability, and power consumption of the CSAC. The reduction of the power consumption and CSAC volumes demands the manufacture of corresponding vapor cells. This overview presents the research development of vapor cells of the past few years and analyzes the shortages of the current preparation technology. By comparing several different vapor cell preparation methods, we successfully realized the micro-fabrication of vapor cells using anodic bonding and deep silicon etching. This cell fabrication method is simple and effective in avoiding weak bonding strengths caused by alkali metal volatilization during anodic bonding under high temperatures. Finally, the vapor cell D2 line was characterized via optical-absorption resonance. According to the results, the proposed method is suitable for CSAC.
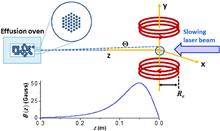
We study a Zeeman slower using the magnetic field generated by a pair of coils for a magneto-optical trap. The efficiency of the Zeeman slower is shown to be dependent on the intensity and frequency detuning of the laser light for slowing the atoms. With the help of numerical analysis, optimal experimental parameters are explored. Experimentally, the optimal frequency detuning and intensity of the slowing beam are explored, and 4 × 107 ytterbium atoms are trapped in the magneto-optical trap.
A vapor cell provides a well-controlled and stable inner atmosphere for atomic sensors, such as atomic gyroscopes, atomic magnetometers, and atomic clocks, and its hermeticity affects the stability and aging of atomic sensors. We present the micro-fabrication of a micro-electromechanical system wafer-level hermit vapor cell based on deep reactive ion etching and vacuum anodic-bonding technology. The anodic-bonding process with the voltage increasing in steps of 200 V had a critical influence on vapor cell hermeticity. Further, the silicon–glass bonding surface was experimentally investigated by a scanning electron microscope, which illustrated that there were no visual cracks and defects in the bonding surface. The leak rate was measured using a helium leak detector. The result shows that the vapor cells with different optical cavity lengths comply with the MIL-STD-883E standard (5 × 10 8 mbar·L/s). Moreover, D2 absorption spectroscopy was characterized via optical absorption. The bonding strength was determined to be 13 MPa, which further verified the quality of the vapor cells.
We present a method to precisely determine the hyperfine structure constants of the rubidium 5D5/2 and 7S1/2 states in a cascade atomic system. The probe laser is coupled to the 5S1/2→5P3/2 hyperfine transition, while the coupling laser is scanned over the 5P3/2→5D5/2(7S1/2) transition. The high-resolution double-resonance optical pumping spectra are obtained with two counter-propagating laser beams acting on rubidium vapor. The hyperfine splitting structures are accurately measured by an optical frequency ruler based on the acousto-optic modulator, thus, the magnetic dipole hyperfine coupling constant A and quadrupole coupling constant B are determined. It is of great significance for the atomic hyperfine structure and fundamental physics research.
We report on the observation of the highly forbidden S10–P30 optical clock transition in laser-cooled Hg199 atoms. More than 95% depletion of cold Hg199 atoms is detected in the magneto-optical trap. Using the free-of-field detection method, the AC Stark shift from the cooling laser is removed from the in-field spectroscopy. At low-power clock laser pumping, the linewidth of the clock spectroscopy is approximately 450 kHz (full width at half-maximum), which corresponds to a Doppler broadening at the atom temperature of 60 μK. We determine the S10–P30 transition frequency to be 1,128,575,290.819(14) MHz by referencing with a hydrogen maser and measuring with a fiber optical frequency comb. Moreover, a weak Doppler-free signal is observed.
Photoassociation via reverse ladder transition controlled by two and four laser pulses is investigated using the time-dependent quantum wave packet method. The calculated results show that the amplitudes of the pulses have an enormous effect on the target population and total yield of association. For the target state with a high energy level, the population of background states can reduce the state-selectivity. Although, the total yield of association is decreased, the four pulses can induce the population transferring to low vibrational levels, and the state-selectivity of the target state is high.
A simple and robust technique is reported to offset lock a single semiconductor laser to the atom resonance line with a frequency difference easily adjustable from a few tens of megahertz up to tens of gigahertz. The proposed scheme makes use of the frequency modulation spectroscopy by modulating sidebands of a fiber electro-optic modulator output. The short-term performances of a frequency offset locked semiconductor laser are experimentally demonstrated with the Allan variance of around 3.9×10 11 at a 2 s integration time. This method may have many applications, such as in Raman optics for an atom interferometer.
We investigate the nonadiabatic spectral redshift of high-order harmonic of He driven by two time-delayed orthogonally polarized laser fields. It is found that the nonadiabatic spectral redshift can be observed by properly adjusting the time delay of the two laser fields when the controlling pulse is added in the raising part of the driving pulse in the vertical direction. That is because the controlling pulse in the vertical direction prevents the ionized electrons from returning to the vicinity of parent ions and then reduces the recombination probability. This leads to the high-order harmonic generated mainly in the falling part of the driving pulse. Meanwhile, we also find that the quantity of redshift can be effectively controlled through accommodating the positive time delays. In addition, this scheme can also be used to produce nonadiabatic spectral blueshift.
Using the classical-trajectory Monte Carlo model, we have theoretically studied the angular momentum distribution of frustrated tunneling ionization (FTI) of atoms in strong laser fields. Our results show that the angular momentum distribution of the FTI events exhibits a double-hump structure. With this classical model, we back traced the tunneling coordinates, i.e., the tunneling time and initial transverse momentum at tunneling ionization. It is shown that for the events tunneling ionized at the rising edge of the electric field, the final angular momentum exhibits a strong dependence on the initial transverse momentum at tunneling. While for the events ionized at the falling edge, there is a relatively harder recollision between the returning electron and the parent ion, leading to the angular momentum losing the correlation with the initial transverse momentum. Our study suggests that the angular momentum of the FTI events could be manipulated by controlling the initial coordinates of the tunneling ionization.
Beam quality degradation during the transition from a laser wakefield accelerator to the vacuum is one of the reasons that cause the beam transport distortion, which hinders the way to compact free-electron-lasers. Here, we performed transition simulation to initialize the beam parameters for beam optics transport. This initialization was crucial in matching the experimental results and the designed evolution of the beamline. We experimentally characterized properties of high-quality laser-wakefield-accelerated electron beams, such as transverse beam profile, divergence, and directionality after long-distance transport. By installing magnetic quadrupole lenses with tailored strength gradients, we successfully collimated the electron beams with tunable energies from 200 to 600 MeV.
We report on an experimental investigation on the dynamic decoherence process of molecular rotational wavepackets during femtosecond laser filamentation based on time-dependent mean wavelength shifts of a weak probe pulse. Details of periodic revival structures of transient alignment can be readily obtained from the measured shifted spectra due to the periodic modulation of the molecular refractive index. Using the method, we measured decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets in N2 and O2 under different experimental conditions. Our results indicate that decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets are primarily determined by the relative population of rotational states in the wave packet and intermolecular collisions, rather than the focusing intensity.
A three-level lambda system driven by multicolor control, pump, and probe fields is investigated. The pump and probe fields are derived from the same laser with opposite propagating directions. Due to the Doppler effect, the zero group-velocity atoms face bichromatic fields, while other atoms face trichromatic fields. The atomic medium shows distinct characteristics and exhibits simultaneous electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) and electromagnetically induced absorption (EIA) at two frequencies. EIT and EIA peaks have a fixed relationship with frequency, which is determined by the Doppler shifts.
A 1470 nm+852 nm two-color (TC) cesium (Cs) magneto-optical trap (MOT) with a 6S1/2-6P3/2-7S1/2 ladder-type system is proposed and experimentally investigated. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first report about the 1470 nm+852 nm Cs TC-MOT. One of the three pairs of the 852 nm cooling and trapping beams (CTBs) in a conventional Cs MOT is replaced with a pair of the 1470 nm CTBs. Thus, the TC-MOT partially employs the optical radiation forces from photon scattering of the 6P3/2 (F′=5) 7S1/2 (F′′=4) excited-state transition (1470 nm). This TC-MOT can cool and trap Cs atoms on both the red- and blue-detuning sides of the two-photon resonance. This work may have applications in cooling and trapping of atoms using inconvenient wavelengths and background-free detection of cold and trapped Cs atoms.
We investigate the transitions between energy levels and parity symmetry in an effective two-level polar molecule system strongly coupled with a quantized harmonic oscillator. By the dressed-state perturbation theory, the transition diagrams between the dressed-state energy levels are presented clearly and show that the odd (even) parity symmetry is broken by the permanent dipole moment (PDM) of the polar molecules. By the analytical and numerical methods, we find that when the coupling strength and the PDM increase, the more frequency components are induced by the counter-rotating terms and PDM.
The environmental perturbation on atoms is a key factor restricting the performance of atomic frequency standards, especially in the long-term scale. In this Letter, we perform a real-time noise distinguish (RTND) to an atomic clock to decrease the uncertainty of the atomic clock beyond the level that is attained by the current controlling method. In RTND, the related parameters of the clock are monitored in real time by using the calibrated sensors, and their effects on the clock frequency are calculated. By subtracting the effects from the error signal, the local oscillator is treated as equivalently locked to the unperturbed atomic levels. In order to perform quantitative tests, we engineer time-varying noise much larger than the intrinsic noise in our fountain atomic clock. By using RTND, the influences of the added noises are detected and subtracted precisely from the error signals before feeding back to the reference oscillator. The result shows that the statistical uncertainty of our fountain clock is improved by an order of magnitude to 2×10?15. Besides, the frequency offset introduced by the noise is also corrected, while the systematic uncertainty is unaffected.
The construction of a two-dimensional magneto–optical trap with hollow cooling and pushing (2D-HP MOT) is reported in detail, and a velocity-tunable cold atomic beam produced by this 2D-HP MOT is demonstrated. The magneto–optical trap system, which is constructed by a transparent quartz tube, is low in price, easy to fabricate and assemble, and convenient for atomic trapping and detection. The mean axial velocity of the cold atomic beam can be tuned from 4.5 to 8 m/s, while the atomic flux remains at a level of 1010 atoms/s. This cold atomic beam source can be applied in the areas of high-precision measurements based on cold atoms.
We report the recent progress of our pulsed optically pumped (POP) vapor cell rubidium clock with dispersive detection. A new compact physics package is made. A rubidium cell with a high precision buffer gases mixing ratio is obtained, and the temperature controlling system is renovated to reduce fractional frequency sensitivity to temperature variation. The resolution of the servo control voltage is also optimized. With these improvements, a clock frequency stability of 3.53×10 13 at 1 s is obtained, and a fractional frequency stability of 4.91×10 15 is achieved at an average time of τ=2000 s.
The photoionization by two elliptically polarized, time delayed attosecond pulses is investigated to display a momentum distribution having the helical vortex or ring structures. The results are obtained by the strong field approximation method and analyzed by the pulse decomposition. The ellipticities and time delay of the two attosecond pulses are found to determine the rotational symmetry and the number of vortex arms. For observing these vortex patterns, the energy bandwidth and temporal duration of the attosecond pulses are ideal.
We demonstrate that the filamentation process is strongly influenced by the polarization state of the driver laser. When the laser polarization changes from linear to circular, the critical power for the self-focusing of a Ti:Sapphire laser (800 nm, 40 fs) in air increases from about 9.6±1.0 to 14.9±1.5 GW, while the second nonlinear refractive index n2 of air decreases from 9.9 × 10 20 to 6.4 × 10 20 cm2/W. We also demonstrate that the luminescence from the neutral nitrogen molecules at 337 nm is dependent on both the laser intensity and plasma density inside the filament.
The carrier envelope phase (CEP) has a direct impact on the physical properties of an isolated attosecond pulse (IAP) and many strong field processes, but it is difficult to measure in reality. Aiming at obtaining more accurate and complete characterization of CEP, we numerically investigate the annular photoelectron momentum spectra of the hydrogen atom ionized by overlapped fields of an IAP and an infrared (IR) pulse. By defining an overlapping parameter, the momentum patterns are classified and optimized for unambiguously measuring the rotation angle of a momentum pattern versus the CEP value. A series of simulations verify its robustness.
We report the Hong–Ou–Mandel (HOM) interference, with visibility of 91%, produced from two independent single photons retrieved from collective atomic excitations in two separate cold-atom clouds with high optical depths of 90. The high visibility of the HOM dip is ascribed to the pure single photon in the Fock state that was generated from a dense-cold-atom cloud pumping by a short pulse. The visibility is always the same regardless of the time response of the single-photon detectors. This result experimentally shows that the single photons retrieved are in a separable temporal state with their idler photons.
A Fourier optics approach can be a concise and powerful tool to solve problems in atom optics. In this report, we adopt it to investigate the kinetic behavior of cold atoms passing through a far red-detuned Gaussian beam. We demonstrate that the aberration has significant influence on the evolution of the atomic cloud, which is rooted in the deviation of the Gaussian profile from the quadratic form. In particular, we observe an intriguing effect analogous to Fresnel’s double prism with cold atoms. The experimental results are in good agreement with the numerical simulation.
We propose a robust scheme that creates a toroidal magnetic potential on a single-layer atom chip. The wire layout consists of two interleaved Archimedean spirals, which avoids the trapping perturbation caused by the input and output ports. By using a rotation bias field, the minimum of the time-averaged orbiting potential is lifted from zero, and then a relatively smooth and harmonic ring trap is formed. The location of the waveguide is immune to the magnetic variations, as it is only determined by the wire layout. The ring waveguide offers an ideal solution to developing a compact and portable atomic gyroscope.
The threshold of a laser-induced breakdown of air is determined experimentally and theoretically. We find that the ionization of air has two steps: the first step is a multi-photon ionization process, which provides enough “seed electrons” to initiate the next step, and the second one is predominated by cascade ionization, which continues to produce free electrons geometrically until the critical free-electron density for breakdown is reached. So a two-step model based on the Morgan ionization model is established to describe the breakdown process. It is found that the time node dividing the two steps is about 9.8 ns in atmospheric air, and the threshold derived from the two-step model proposed here is more consistent with the experimental results than traditional ionization model.
We demonstrate a magneto-optical trap (MOT) with counter-propagating two-color cooling beams in a cesium 6S1/2 6P3/2 8S1/2 (852.3+794.6 nm) atomic system. Based on the conventional MOT due entirely to the 852.3 nm cooling laser’s scattering forces, we replace one of the six 852.3 nm cooling beams with a 794.6 nm cooling beam. Our two-color MOT can efficiently cool and trap atoms from the red to blue detuning sides of two-photon resonance without pre-cooling. The technique is promising for the direct generation of correlated photon pairs in a two-color MOT based on diamond-configuration four-wave mixing.
We theoretically investigate multiple electron rescatterings in high-order harmonic generation with a wide range of driving laser wavelengths. In order to obtain a clear and intuitive insight, the time-frequency analysis of the dipole acceleration calculated by the numerical solution of the time-dependent Schr dinger equation is performed and compared with the classical electron trajectory calculation. The result shows that in the mid-infrared regime, the high-order electron trajectory associated with multiple rescatterings plays a more important role than the usually referred-to “long and “short” electron trajectories. To provide quantitative evidence, the strong-field approximation is used to calculate the yield ratio of the high-order harmonic generation from the first rescattering and the multiple rescatterings.
From a classical dynamic simulation, we find the kinetic energy of the electrons generated during laser plasma generation depends on the laser polarization and intensity. The electron kinetic energy reaches its maximum with a fixed laser intensity for circularly polarized laser pulse. The fluorescence spectra at 380.4 nm from N2 and 391.3 nm from N2+ are measured; these are generated by both the direct excitation and electron collision excitation. The electron collision excitation is determined by the electron energy and reaches the maximal with a circularly polarized pulse.
We experimentally and theoretically demonstrate that the property (odd or even) of generated harmonics can be selected by manipulating the macroscopic phase-matching conditions based on a three-color laser field. Only odd or even harmonics can be made dominant by changing the focal position and adjusting the gas pressure. These results indicate that the odd-even property of the generated harmonics can be controlled by using the multi-color laser field with macroscopic phase-matching.
We experimentally demonstrate N2+ lasing actions at the wavelengths of 353.3, 353.8, and 354.9 nm using a circularly polarized femtosecond laser. The three laser lines correspond to the B2Σu+(v′=5,4,3)→X2Σg+(v=4,3,2) transitions, respectively. Particularly, we reveal the pressure-dependent gain dynamics of these lasing actions from highly excited vibrational states with a pump–probe scheme. Our experimental results confirm that electron collisional excitation plays an important role in the establishment of a population inversion of N2+ lasing at these wavelengths.
We report a novel nonresonant magneto-optical effect in cold atoms and present the optimized parameters of the biased magnetic field, the incident probe light intensity, and the probe detuning to obtain the maximal signal of the magneto-optical rotation. This detection scheme may further improve the stability of the cold atom clock.
A sideband-controllable soliton mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser is successfully demonstrated utilizing the nonlinear polarization rotation technique. The sidebands can be produced or suppressed by performing simple polarization light tuning with a polarization controller. It is believed that the elimination of the sidebands is due to the dispersive waves that are filtered out by the polarization-dependent isolator in the resonator. With the elimination of the Kelly sidebands, the obtained 3 dB bandwidth is 10.6 nm and the attainable pulse duration is 0.86 ps. In this experiment, it is proven that the existence of Kelly sidebands limits the attainable pulse duration.
We report experimental progress in weakening the frequency difference lock-in phenomenon in a Y-shaped cavity dual-frequency laser. A cube coil pair is chosen to provide a uniform magnetic field for tunability and uniformity of magnetic field strength. When the transverse magnetic field intensity is 9 mT, the frequency difference lock-in phenomenon is evidently weakened and the frequency difference can be continuously tuned in the range of 0.12 MHz to 1.15 GHz. Moreover, the relationship between the minimal frequency difference and magnetic field intensity are investigated and discussed. Then a Y-shaped cavity dual-frequency laser is expected to be utilized as an optimum light source for heterodyne interferometric sensing and precise laser measurement.
A stable, single-longitudinal-mode, nanosecond-pulsed Nd:YAG laser with a laser-diode dual-end pumping arrangement is constructed. Injection seeding is performed successfully by utilizing a RbTiOPO4 crystal as the intracavity phase modulator to change the optical length of the slave cavity based on the delay-ramp-fire technique. The laser generates 9.9 mJ of pulse energy with a 16 ns pulse duration at a 400 Hz repetition rate. A near-diffraction-limit laser beam is achieved with a beam quality factor M2 of approximately 1.2. The frequency jitter is 1.5 MHz over 2 min, and the fluctuation of the output pulse power is 0.3% over 23 min.
A diode-end-pumped tunable twisted-mode cavity Tm, Ho:YAG laser with single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) operation is demonstrated in this Letter. The maximal SLM output power is 106 mW with a slope efficiency of 4.86%. The wavelength can be changed from 2090.38 to 2097.32 nm by tuning the angle of an etalon.
An efficient two-stage KTiOAO4 optical parametric amplifier (OPA) system with walk-off-compensating alignment is designed. By introducing an extra time delay between the pump pulse and the signal pulse, this OPA architecture is capable of obtaining high optical conversion efficiency and high signal gain simultaneously. Finally, a maximum gain of 98 at the 1.57 μm wavelength is obtained with the signal beam quality of M2 around 5.6. The efficiency of the optical conversion from 1.064 to 1.57 μm is around 26%.
We report a simple, cost-effective and repeatable method for fabricating a large area and uniform substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). The silicon, micromachined by a femtosecond laser, is coated with gold film and then treated through the dewetting process. The morphology shows a higher electric field enhancement due to light trapping. The enhancement factor of the SERS substrate is 9.2×107 with a 5 nm-thick film coated. Moreover, it also exhibits a uniform signal through Raman mapping and chemical stability with the greatest intensity deviation of 6% after a month. The proposed technique provides an opportunity to equip microchips with the SERS capabilities of high sensitivity, chemical stability, and homogeneous signals.
Due to the excellent electro-optic properties of lead lanthanum zirconium titanate ((Pb,La)(Zr,Ti)O3, PLZT), compact 1×2 and 1×4 PLZT optical switches with a high response speed are proposed and fabricated successfully in this Letter. By introducing a thin isolating layer between the waveguides and the electrodes, the absorption loss of the fabricated 1×2 PLZT switch caused by the electrodes is reduced 8.9 dB with a relatively low driving voltage. The 1×2 PLZT switch shows an insertion loss of 18.3 dB and crosstalk of 20.5 dB at an applied voltage of 9.5 V. The fabricated 1×4 switch array shows an insertion loss of 20.7 dB and a crosstalk of 20.5 dB at an applied voltage of 13 V. The response time of the switches is less than 27 ns, and the device’s size is only 15 mm×6 mm. The switches can be used in optical communication systems.
A CO2 sensor for capnography, based on a hollow waveguide (HWG) and tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS), is presented; the sensor uses direct absorption spectroscopy and requires neither frequent calibration nor optical filters, giving it a significant advantage over existing techniques. Because of the HWG, the CO2 measurement achieved a concentration resolution of 60 ppm at a measurement rate of 25 Hz, as characterized by Allan variance. The length of the HWG was selected to efficiently suppress the optical fringes. This setup is perfectly suited for the detection of CO2 by capnography, and shows promise for the potential detection of other breath gases.
The exoplanet search is one of the most exciting research fields in astrophysics. The Antarctic Bright Star Survey Telescope (BSST), capable of continuous exoplanet observation on polar nights, is a Ritchey–Chretien telescope with a three-lens field corrector, and has a 300 mm aperture, 2.76 focal ratio, and a wavelength coverage ranging from 0.36 to 1.014 μm. Equipped with a 4 k×4 k and 12 μm/pixel CCD camera, the BSST can gain a field of view of 4.8°. This Letter presents the optical design, tolerance analysis, and the alignment plan for the BSST, and the test observation results.
This Letter proposes to apply full-color computer-generated holograms to the virtual image projection system so that the viewers can comfortably view floating images. Regarding the spatial division and distribution operation, a modified Gerchberg–Saxton algorithm is used for acquiring the phase infographics, which are input into the spatial light modulator for the reconstructed projection. Such a virtual image projection system could reach the vertical angle of view of 15°–75° and the horizontal angle of view 360°, and the mixed-light modulating proportion contains a 3 mW red light laser, a 2 mW green light laser, and a 2.6 mW blue light laser to achieve the full-color mixed-light proportion with a speckle contrast of 6.65%. The relative diffraction efficiency and root mean square error of the reconstructed image are 95.3% and 0.0524, respectively.
An adaptive digital backward propagation (ADBP) algorithm is proposed and experimentally demonstrated based on the variance of the intensity noise. The proposed algorithm can self-determine the unknown nonlinear coefficient γ and the nonlinear compensation parameter ξ. Compared to the scheme based on the variance of phase noise, the proposed algorithm can avoid the repeated frequency offset compensation and carrier phase recovery. The simulation results show that the system’s performance compensated by the proposed method is comparable to conventional ADBP schemes. The performance of the proposed algorithm is simulated in 40/112 Gb/s polarization-division multiplexing (PDM)-quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) and 224 Gb/s PDM-16-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) systems and further experimentally verified in a 40 Gb/s PDM-QPSK coherent optical communication system over a 720 km single-mode fiber.
In an experiment on the round-trip fiber transfer of joint frequency and time signals based on wavelength-division multiplexing technology, a specific bidirectional erbium-doped fiber amplifier (Bi-EDFA) with low noise and high symmetry simultaneously is designed and applied to compensate for the loss of the link. The Allan deviation (ADEV) deterioration of the 1 GHz frequency signal induced by the Bi-EDFA is only 8×10 15 at 1 s and 9×10 18 at 104 s in the forward direction, and is 1.7×10 14 at 1 s and 1.2×10 17 at 104 s in the backward direction. The degraded time deviation (TDEV) caused by the asymmetry of the Bi-EDFA is only 0.8 ps at an average time of 103 s. With the proposed Bi-EDFA, in the field experiment on the 110 km fiber transfer of joint frequency and time signals, the ADEV of the 1 GHz frequency signal is 7.3×10 14 at 1 s and 2.5×10 17 at 104 s. The TDEV of the 1 pulse per second time signal is 6.8 ps with an average time of 1
A new miniature spectrometer with two entrance slits is proposed to expand the spectral band. The proposed spectrometer is designed such that the two entrance slits share the same concave grating and detector array. The two slits are located at different positions such that the spectral range of the same light source incident on the detector array varies greatly between the two slits. Only one of the two slits is illuminated at a given time; as such, the two spectral ranges are sequentially measured. Theoretical calculation and experimentation are conducted to verify the proposed design.
We present a simple, robust, space-adjustable dark magneto-optical trap (MOT) for the efficient production of heteronuclear molecules. Double-mixed beams made up of repumping beams and depumping beams propagate in nearly opposite directions in the dark MOT. This optical arrangement can easily adjust the spatial positions of two clouds by changing the power ratio of the two repumping beams, and ensure a good overlap, which is very necessary for the production of heteronuclear molecules. The imaging of cold atoms by camera and the collision-induced loss rate obtained by recording the loading curve of the cold atoms show that we obtain a perfect overlap of atom clouds. The number of RbCs molecules with the double-mixed beams is improved by 70%, which is higher than the one with the single-mixed beam.
We report experiments on the observation of the S01 P03 transition spectrum of Sr88 in the Lamb-Dicke regime. After going through a two-stage magneto-optical trap (MOT), Sr88 cold atoms with number of about 1×105 and a longitudinal temperature of 8.4 μK are loaded into a one-dimensional (1D) optical lattice, which is realized with a semiconductor laser at 813.4 nm. Using the magnetic field-inducing P13 state mixing into P03 state, the spectroscopy of the S01 P03 transition with a linewidth of 180 Hz is detected.
We develop a new algorithm to evaluate the thermal features of a rubidium-vapor cell and a cesium-vapor cell pumped by the laser diode. The theoretical model is based on the principles of both heat transfer and laser kinetics. The obtained population density distribution and the radial temperature distribution are analyzed for both types of cells. It is thought that the theoretical results are logically reasonable and the mathematical precision is satisfactory in designing a real diode-pumped alkali laser (DPAL). The methodology is valuable in the construction of a high-powered DPAL in the future.
A new polarization gating is demonstrated by our principle-of-proof experiment, which is theoretically proposed to generate the isolated or double attosecond pulses with the multi-cycle driving laser pulse in the previous work [Optics Express. 20, 5196 (2012)]. In the experiment, the polarization gating is formed by two orthogonally-polarized linearly chirped multi-cycle laser pulses, and the spectral bandwidths of the harmonics are broadened by more than two times, which agree with the previous theoretical work.
We experimentally investigate the high-order harmonic generation in argon gas cell driven by a multi-cycle broadband infrared laser pulse from a tunable optical-parametric-amplifier (OPA) source. The generation of high-order harmonic continuum with the cut-off photon energy up to 110 eV is observed by tuning the chirp of the 800-nm laser pulse which pumps OPA source. The generation of harmonic continuum is understood in terms of the two-hump structure of the OPA output spectrum and the optimal relative phase of the two humps. The demonstrated scheme is of importance for the generation of extreme ultraviolet (XUV) continuum at higher photon energy region.
In this letter, we discuss the increase in the average cluster size by lowering the stagnation temperature of the methane (CH4) gas. The Coulomb explosion experiments are conducted to estimate the cluster size and the size distribution. The average CH4 cluster sizes Nav of 6 230 and 6 580 are acquired with the source conditions of 30 bars at 240 K and 60 bars at 296 K, respectively. Empirical estimation suggests a five-fold increase in the average size of the CH4 clusters at 240 K compared with that at room temperature under a backing pressure of 30 bars. A strong nonlinear Hagena parameter relation (\Gamma *\propto T^{-3.3}) for the CH4 clusters is revealed. The results may be favorable for the production of large-sized clusters by using gases at low temperature and high back pressures.
We investigate the optical bistability (OB) in a duplicated two-level system contained in a ring cavity. The atoms are driven by two orthogonally polarized fields with a relative phase. The OB behavior of such a system can be controlled by the amplitude and the relative phase of the coupling field, and it is possible to switch between bistability and multistability by adjusting the relative phase.
Population ratios between excited states are measured to build the excited state Faraday anomalous dispersion optical filter (ESFADOF). We calculate these values between the excited states according to the spontaneous transition probabilities using rate equations and the measured intensities of fluorescence spectral lines of He atoms in an electrodeless discharge lamp in the visible spectral region from 350 to 730 nm. The electrodeless discharge lamp with populations in excited states can be used to realize the frequency stabilization reference of the laser frequency standard. This lamp can also build ESFADOFs for submarine communication application in the blue-green wavelength to simplify the system without the use of a pump laser.
We experimentally demonstrate a simple modulation-free scheme for offset locking the frequency of a laser using buffer gas-induced resonance. Our scheme excludes the limitation of low diffraction efficiency and laser input intensity when an acousto-optic modulator is applied to shift the laser frequency from the resonance. We show the stabilization of a strong 795-nm laser detuned up to 550 MHz from the 87Rb 5S1/2F=2->5P1/2 F'=2 transition. The locking range can be modified by controlling the buffer gas pressure. A laser line width of 2 MHz is achieved over 10 min.
We theoretically investigate quantum transport of a two-component quantum gas in a disordered potential and predict a unique disorder-induced splitting of a matter wavepacket. We also demonstrate that the splitting of the mobile component originates from the inter-component interaction and the disordered potential on the localized component.
A method that uses radio frequency (RF) spectroscopy to evaluate the alignment of an optical lattice is proposed and demonstrated. A one-dimensional (1D) optical lattice is applied along the long axis of a cigar-shaped Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) in a magnetic trap. The RF spectra of condensates with and without the optical lattice are analyzed, measured, and compared with the condition in which the lattice is misaligned with the BEC. The proposed method greatly optimizes the optical alignments of the lattices.
We cool 85Rb atoms in an integrating sphere directly from a vapor background using diffuse light generated by multiple reflections of laser beams in the inner surface of the integrating sphere. We compare and analyze the different features of cold 85Rb atoms and cold 87Rb atoms in diffuse light cooling, which are important in applying 85Rb and 87Rb isotopes in many experiments on testing fundamental physics.
Wave packet propagation techniques are used to find experimentally reliable laser parameters that yield optimal production. The photoionization and photodissociation dynamics of sodium iodine molecules are interpreted into several channels. Several frequencies are found to be suitable for NaI molecules during the photoionization and dissociation processes. Photon-dressed excited states and electron-dressed ionic continuum states facilitate the search for available laser parameters.
We analyze entanglement dynamics and transfer in a system composed of two initially correlated two-level atoms, in which each atom is coupled with another atom interacting with its own reservoir. Considering atomic dipole-dipole interactions, the results show that dipole-dipole interactions restrain the entanglement birth of the reservoirs, and a parametric region of dipole-dipole interaction strength exists in which the maximal entanglement of two initially uncorrelated atoms is reduced. The transfer of entanglement shows obvious different behaviors in two initial Bell-like states.
The Ramsey fringe contrast of a pulsed optically pumped cold atom clock is strongly affected by the transverse decay of the atomic sample. This letter calculates the Ramsey fringe with focus on transverse decay, and analyzes the Ramsey fringe contrast with different transverse decay rates. By fitting the experimental data, we obtain the transverse decay rate in a cold atom sample at an approximate value of 30.5 s-1, which is much smaller than that in a cell.
A periodic layered medium, with unit cells consisting of a dielectric and an electromagnetically-induced transparency (EIT)-based atomic vapor, is designed for light propagation manipulation. Considering that a destructive quantum interference relevant to a two-photon resonance emerges in EIT-based atoms interacting with both control and probe fields, an EIT-based periodic layered medium exhibits a flexible frequency-sensitive optical response, where a very small variation in the probe frequency can lead to a drastic variation in reflectance and transmittance. The present EIT-based periodic layered structure can result in controllable optical processes that depend sensitively on the external control field. The tunable and sensitive optical response induced by the quantum interference of a multi-level atomic system can be applied in the fabrication of new photonic and quantum optical devices. This material will also open a good perspective for the application of such designs in several new fields, including photonic microcircuits or integrated optical circuits.
The 4f7 6s(9S)np 8PJ (J=5/2, 7/2, 9/2) Rydberg series converging to the first ionization limit 4f7 6s 9S4 of the Eu atom using the three-step laser excitation and electric-field-ionization (EFI) method are studied. First, the Eu atom is excited from the 4f7 6s2 8So7/2 ground state to the 4f76s7s 8So7/2 state through the 4f7 6s6p 10P9/2 state by the first two dye lasers. Next, it is populated to many higher-n members of the 4f7 6s(9S)np 8PJ Rydberg series by the third dye laser whose wavelength is scanned within a certain range. Finally, the atom in these higher-n states is ionized by the external pulsed electric field. With the field strength up to 2 kV/cm, we can detect the atom in 4f76s(9S)np 8PJ states with n>40. With the given laser line width, the level energies of Rydberg states with n as high as 72 can be determined. We not only confirm the previous data on the 4f76s(9S) np 8PJ Rydberg series, but also extend the n-value assignment significantly by detecting more states.
The Ryderberg electronic wave packet dynamics of hydrogen atom near helium surface in an electric field is investigated using the semiclassical method. The autocorrelation function is calculated when the photoionized electron is excited by a short laser pulse for different atom-surface separations. The results show that new recurrences appear because of the helium surface, and the number of recurrent peaks increases with the decrease in atom-surface distance. The new feature is ascribed to the bifurcation of new closed orbits in the classical dynamics of the photoionized electron. Therefore, surface properties have a significant effect on the spectrum of nearby atoms or ions.
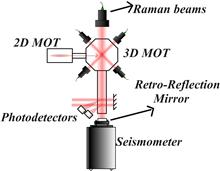
A simple improved structure is designed to trap and launch two cold atomic balls vertically at the same time, which works like "two fountains", but is more compact since most components of the "two fountains" are shared. It is expected to improve the stability of the fountain markedly.
Multi-reference configuration interaction is used to produce potential energy curves (PECs) for the excited B1\Pi state of KH molecule. To investigate the correlation effect of core-valence electrons, five schemes are employed which include the different correlated electrons and different active spaces. The PECs are fitted into analytical potential energy functions (APEFs). The spectroscopic parameters, ro-vibrational levels, and transition frequencies are determined based on the APEFs and compared with available experimental and theoretical data. The molecular properties for B1| obtained in this letter, which are better than those available in literature, can be reproduced with calculations using the suitable correlated electrons and active space of orbitals.
The optical properties of a five-level atomic system composed of a 'Lambda'-type four-level atomic and a tripod four-level atomic systems are investigated. It is found that the behaviors of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) and group velocity can be controlled by choosing appropriate parameters with the interacting dark resonances. In particular, when all the fields are on resonance, the slow light at the symmetric transparency windows with a much broader EIT width is obtained by tuning the intensity of the coupling field in comparison with its sub-system, which provides potential applications in quantum storage and retrieval of light.
A deuterium cluster jet produced in the supersonic expansion into vacuum of deuterium gas at liquid nitrogen temperature and moderate backing pressures is studied by Rayleigh scattering techniques. The experimental results show that deuterium clusters can be created at moderate gas backing pressures ranging from 8 to 23 bar, and a maximum average cluster size of 350 atoms per cluster is estimated. The temporal evolution of the cluster jet generated at the backing pressure of 20 bar demonstrates a two-plateau structure. The possible mechanism responsible for this structure is discussed. The former plateau with higher average atom and cluster densities is more suitable for the general laser-cluster interaction experiments.
Considering the changes of the geometric shielding effect in a molecule as the incident electron energy varing, an empirical fraction, which is dependent on the incident electron energy, is presented. Using this empirical fraction, the total cross sections (TCSs) for electrons scattering from complex polyatomic molecules C2F4 and SO2 are calculated over a wide energy range from 30 to 5000 eV together with the additivity rule model at Hartree-Fock level. In the TCS calculations, the atoms are presented by the spherical complex optical potential, which is composed of static, exchange, polarization and absorption contributions. The quantitative TCSs above 100 eV are in good agreement with those obtained by experiments and other theories. It is proved that the empirical fraction, which exhibits the TCS contributions of shielded atoms in a molecule at different energies, is reasonable.
An investigation of the cluster size dependence of the maximum energy of protons ejected from explosion of methane clusters in an intense femtosecond laser field has been conducted on the basis of the cluster size estimation by Rayleigh scattering measurements. The interaction of a 2*10^(16)-W/cm2 intense laser pulse (790 nm, 60 fs) with the methane clusters revealed that the clusters were Coulomb exploded and the maximum energy (E_(max)) of the protons produced was linearly proportional to the square of the cluster radius (r_(c)^(2)). In a cluster size range, with the methane cluster radii up to about 3 nm, the established relation of E_(max) and r_(c)^(2) was found to be E_(max) (keV) = 3.3+0.75r_(c)^(2) (nm2), in good agreement with the simulation results. This demonstrated that Coulomb explosion of ionic clusters (C^(+4)H^(+)_(4))_(n) took place following the cluster vertical ionization in the laser-cluster interaction.
The total (elastic plus inelastic) cross sections for positron scattering from N2 and CO2 over the incident energy range from 30 to 3000eV are calculated using the additivity rule model at Hartree-Fock level. A complex optical model potential modified by incorporating the concept of bonded atom, which takes into account the overlapping effect of electron clouds between two atoms in a molecule, is employed to calculate the total cross section of positron-molecule scattering. The calculated total cross sections are in good agreement with those reported by experiments and other theories over a wide energy range.
Total cross sections (TCSs) of electrons scattering from triatomic molecules over the energy range from 30 to 5000 eV are investigated employing a new semi-empirical formula. The TCSs of electrons scattering from triatomic molecules SO2, NO2, and CO2 are calculated. The quantitative TCSs are in good agreement with those obtained by experiments. It is shown that the results derived from the semi-empirical formula are much closer to the measurements than other calculations.
The behavior of population transfer in an excited-doublet four-level system driven by linear polarized few-cycle ultrashort laser pulses is investigated numerically. It is shown that almost complete population transfer can be achieved even when the adiabatic criterion is not fulfilled. Moreover, the robustness of this scheme in terms of the Rabi frequencies and chirp rates of the pulses is explored.
For a weakly and periodically driven two-component Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) the Melnikov chaotic solution and boundedness conditions are derived from a direct perturbation theory that leads to the chaotic regions in the parameter space. Differing from the usual results, the chaotic regions depend on the initial conditions directly and can be controlled by setting the initial phase and modulating the frequency and amplitude of laser. It is demonstrated that the order-chaos transitions can be controlled by tuning the laser frequency only.
We propose a novel array of controllable double-well magnetic microtraps for cold atoms by using an array of square current-carrying wires and two additional bias magnetic fields. Arrays of double layer magneto-optical traps (MOTs) and Ioffe traps can be constructed by using same wire configurations and different currents and bias fields. Furthermore, the array of double-well magnetic microtraps can be continuously evolved as an array of single-well magnetic microtraps by reducing the currents in the wires. Our study shows that our scheme can be used to realize a controllable double-layer magnetic lattice with cold atoms, to form array of Bose-Einstein condensations (BECs), or to study atom interference, and so on.
The accurate dissociation energy and equilibrium geometry of the b3Π state of 7LiH molecule is calculated using a symmetry-adapted-cluster configuration-interaction method in full active space. And the calculated results are 0.2580 eV and 0.1958 nm for the dissociation energy and equilibrium geometry, respectively. The whole potential energy curve for the b3Π state is also calculated over the internuclear separation range from about 0.10 to 0.54 nm. The results are fitted by the Murrell-Sorbie function. It is found that the Murrell-Sorbie function form, which is mainly used to fit the ground-state potential energy function, is well suitable for the excited triplet b3Π state. The vertical excitation energy from the ground state to the b3Π state is calculated to be 4.233 eV. Based on the analytic potential energy function, the harmonic frequency of 610.88 cm^(-1) about this state is firstly estimated. Compared with other theoretical results, this work is the most complete effort to deal with the analytic potential energy function and the harmonic frequency of this state.
We propose a novel scheme to guide cold polar molecules on the surface of an insulating substrate (i.e., a chip) using a static electric field generated by the combination of a pair of parallel charged wires and a grounded metal plate. We calculate the spatial distributions of the electric fields from the above charged-wire layout and their Stark potentials for cold CO molecules, and analyze the relationships between the electric field and the parameters of the charged-wire layout. The result shows that this charged-wire scheme can be used to guide cold polar molecules in the weak-field-seeking state and to form various molecule-optical elements, even to realize a single-mode molecular waveguide on a molecule chip under certain conditions.
We investigate the energy spectrum of fermionized bosonic atoms, which behave very much like spinless noninteracting fermions, in optical lattices by means of the perturbation expansion and the retarded Green's function method. The results show that the energy spectrum splits into two energy bands with single-occupation; the fermionized bosonic atom occupies nonvanishing energy state and left hole has a vanishing energy at any given momentum, and the system is in Mott-insulating state with a energy gap. Using the characteristic of energy spectra we obtained a criterion with which one can judge whether the Tonks-Girardeau (TG) gas is achieved or not.
A complex optical model potential correlated by the concept of bonded atoms, which considers the overlapping effect of electron clouds between two atoms in a molecule, is firstly employed to calculate the absolute differential cross sections, the integrated and momentum transfer cross sections for electrons scattered by O2 at intermediate and high energies by using additivity rule model at Hartree-Fock level. In the study, the complex optical model potential is composed of static, exchange, correlation polarization plus absorption contributions. The quantitative absolute differential cross sections, the integrated and momentum transfer cross sections are obtained. Compared with available experimental data, this approach presents good results. It is shown that the additivity rule model together with the complex optical model potential correlated by the concept of bonded atoms is completely suitable for the calculations of the absolute differential cross sections, the integrated and momentum transfer cross sections.
The interaction of intense femtosecond laser pulses with rare gas clusters was studied experimentally, the time-of-flight spectra of ions from exploding clusters at different gas densities have been measured. It is found that while the relative components of ions in low and high energy of the ion energy spectrum decrease with the increase of the gas density, the average ion energies are the same for different gas densities, which indicates that the effect of gas density on laser-cluster interaction is not important under our experimental conditions.
We start from the intensity distribution of a standing wave (SW) laser field and deduce the classical equation of atomic motion. The image distortion is analyzed using transfer function approach. Atomic flux density distribution as a function of propagation distance is calculated based on Monte-Carlo scheme and trajectory tracing method. Simulation results have shown that source imperfection, especially beam spread, plays an important role in broadening the feature width, and the focus depth of atom lens for real atomic source is longer than that for perfect source. The ideal focal plane can be easily determined by the variation of atomic density at the minimal potential of the laser field as a function of traveling distance.
A fluorescence detection scheme is applied to image an atomic beam. Using two laser diodes as the sources of detection light and pumping light respectively, the fluorescence image of the atomic beam is then observed by a commercial CCD-camera, which is corresponding to the atomic state and velocity distribution. The detection scheme has a great utilization in the experiments of cold atoms and atomic optics.
Two-photon laser-induced fluorescence spectrum (TP-LIF) of NO is obtained with a Nd:YAG pumped optical parametric generator and amplifier as radiation source. Spectral intensity distribution shows that the electronic transition moment for NO (A^(2)∑ → X^(2)∏) transition varies significantly with inter-nuclear distance. The variation relationship of the electronic transition moment versus inter-nuclear distance is deduced with polyminal fit procedure. The spontaneous radiative coefficients for NO (A^(2)∑ → X^(2)∏) transition from ν' = 0, 1 are obtained by combing this transition moment variation with the measurements of spontaneous radiative lifetime.
Polarization spectra of rubidium atoms were investigated with different uncrossed angles between the polarizer and the analyzer. The variation of the spectra was derived theoretically as a function of arbitrary angle, and measured experimentally for different angles. The spectral profile of D_(2) line of rubidium was further used to stabilize the frequency of a diode laser. It was demonstrated that the laser linewidth was reduced to 2 MHz.
Stimulated-Raman-adiabatic-passage (STIRAP) process provides an effective technique to transfer electron population from an initial state (e.g. ground state) to excited final state for both atoms and molecules. In this paper, we present the results of the study on electron population transfer in three level system. We have analyzed the effects of various conditions on the transfer process, such as the time delay of the two laser beams, two-photon off-resonance, one-photon off-resonance and the change of relative laser intensity. The numerical result is compared with experiment, and the reasons for the effects are also given.
The resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) spectrum of NO has been obtained in the range of 420 - 480 nm with a Nd:YAG pumped optical parametric generator and amplifier. The spectral lines can be attributed to NO X^(2)(v" = 0; 1) → A^(2)Σ(v' = 0; 1) transitions. In this wavelength range, NO molecules are ionized via the resonant intermediate state A^(2)Σ^(+) and by a (2 + 2) REMPI process. The dependence of ion signals on laser intensity and gas pressure is discussed. The variation of the ionization signal versus laser intensity is near quartic. This is in good agreement with theory.
Penning type discharge was adopted to excite helium atoms. It is suitable for generating high density of metastables at a range from 0.1 mTorr to 0.5 Torr. The highest metastable density of 3.5 * 10^(10) cm^(-3) was observed at a static gas pressure of 0.5 Torr. The highest fraction of metastables (N_(2^(1)S) = N_(He)) of 10^(-3) in a low gas pressure was obtained. The variation of the magnetic field strength on the discharge does not result in a significant density change of the metastable helium atoms. When no magnetic field was applied, no discharge took place.
The quantum dynamic behavior of the system composed of V-type three-level atomic Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) interacting with two-mode coherent light field has been studied. The results show that the atoms of V-type three-level atomic BEC, which are excited to higher-level states under the action of light field, still keep their properties of coherent states. It demonstrates theoretically that two-mode atomic laser may be prepared by V-type three-level atomic BEC.
We investigate the emission spectra of a Ξ-type three-level atom interacting with a single-mode optical field in an ideal cavity filled with a Kerr medium and discuss the structure of emission spectrum when the optical field is initially in a pure number state and a coherent state, respectively. It is shown that the structure of emission spectrum depends not only on the photon number distribution, but also on the strength of incident field and the coupling of Kerr medium to the field.
A model complex optical potential rewritten by the conception of bonded atom, which considers the overlapping effect of electron cloud, is employed to calculate the total (elastic + inelastic) cross sections with simple molecules (N_(2), O_(2), NO_(2), NO, N_(2)O) consisting of N & O atoms over an incident energy range of 100 - 1600 eV by the use of additivity rule at Roothaan-Hartree-Fock level. In the study, the complex optical potential composed of static, exchange, correlation polarization plus absorption contributions firstly uses bonded-atom conception. The qualitative results are compared with experimental data and other calculations wherever available and good agreement is obtained. The total cross sections of electronmolecule scattering above 100 eV can be successfully calculated.